The Indian Government has finally nodded in affirmation for the creation of a National Carbon Market.
India’s Trading Landscape is changing dramatically due to uproars in the global setting & also because of the density in the trade that India upholds. The EU is mandating a Carbon Disclosure Report on all imports & also initiating a Carbon Tax. Australia, the US, and all major economies are now shifting interests to Sustainability in Business. In light of this new & rapid government, introducing a National Trade Market is a key step in furthering a much-required decarbonisation of the Heavy Industries, trading transformations in the country and abroad, and a wide impact on the overall international trading scapes.
A planned National Carbon Market is announced to be voluntary at the initiation which will lead to a smoother transition towards a mandatory cap-and-trade system.
“A Carbon Market creates an incentive for more sectors and individual corporations to transition [to low-carbon fuels & operations].”
– Vibhuti Garg, Energy Economist (IEEFA- Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis)
Let us now delve deep into what all this is & what does it indicate for the future!
What is the Carbon Trade Market and How does it work?
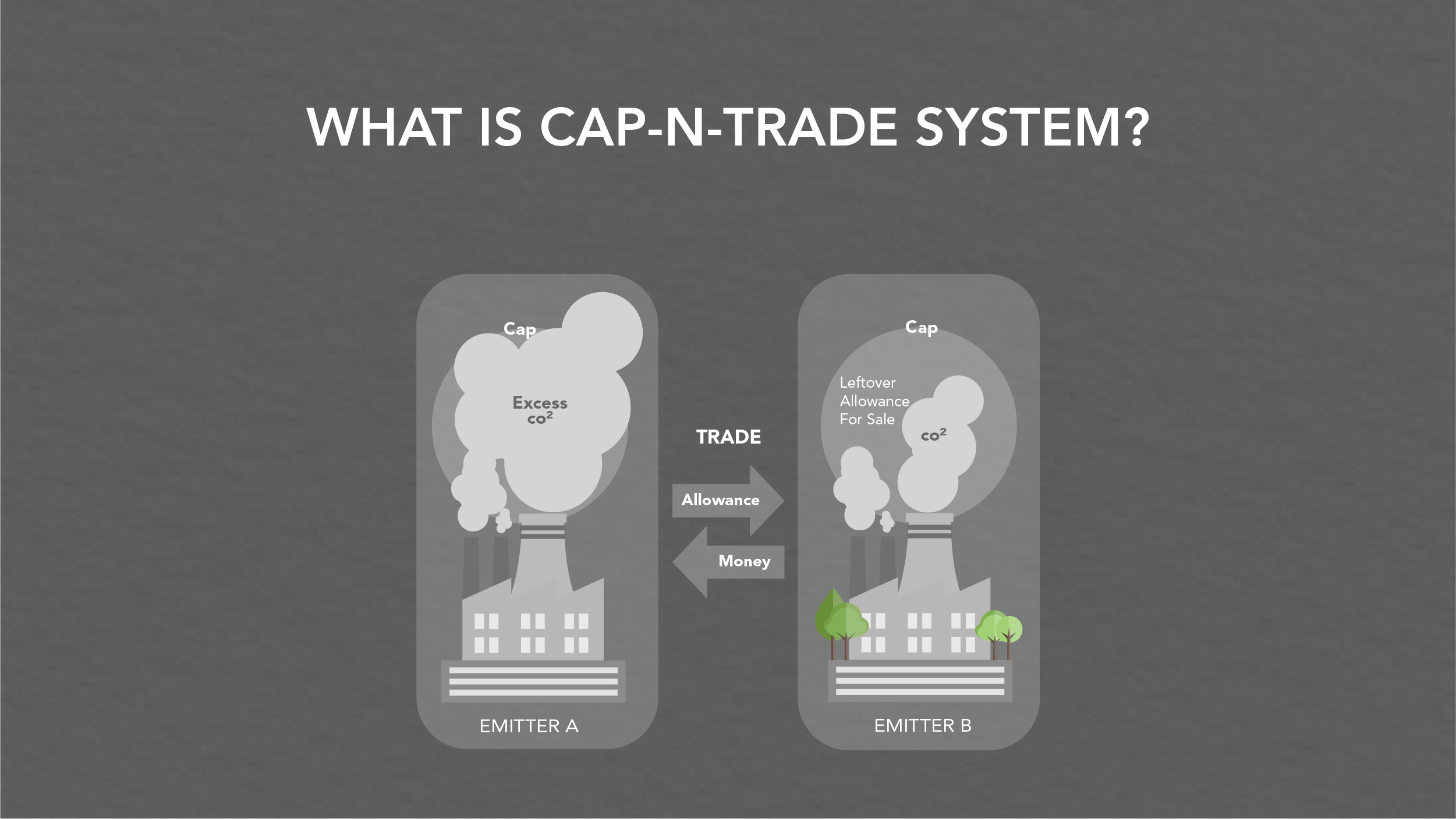
As we know the carbon trade market has been set up formally with a single-point aim to curb CO2 emissions. There are two components of this market that act as an effective system to decarbonize. The market has a system called Cap and trade.
Under this system, the government puts a limit on the carbon emissions by the industries. They set a target and then divide that target into allowances, these allowances are then distributed among the industries. These allowances are termed Carbon credits.
One Carbon Credit is equivalent to One ton of Carbon dioxide or any other GHG (Green House Gases). This is a set limit for industries to emit carbon and hence acts as a Cap. One carbon credit can be priced between 15 dollars and 125 dollars. Their price can vary on the basis of the supply-demand mechanisms.
The company that looks for alternative ways should reduce its carbon emissions within the cap can sell its excess carbon credits to other companies that need more carbon credits. And this is how the companies can trade among themselves and regulate the market.
Why is the National Carbon Trade Market important?
Carbon trading is a significantly effective system that works in controlling carbon emissions. Earlier, at the time of acid rain in America due to the excessive emission of sulfur dioxide, carbon trading played a vital role in lowering the emission.
Hence, the government and regulators are eyeing its establishment to decarbonize the Earth. Cap and trade is a system that puts a limit on carbon emissions lowering the rate and helping governments across the globe to achieve their target of net zero carbon emissions.
This system minimizes government intervention and encourages industries to look for an innovative and effective way to lower their carbon emissions so they have to buy fewer carbon credits.
Now, the question arises of how this market is helping businesses. Here is the answer!
What is India’s initiative on the Carbon Trade Market?
A bill passed in supporting the launch of the Carbon Trade Market in India. The launch is possible by 2023. There will be three phases for the Carbon Trade Market.
First Stage- Harnessing for India’s Carbon Trade Market
The first stage will focus on increasing the demand by taking ESCerts and RECs as a base. Perform, Achieve, and Trade is a scheme that is a market-based tool under the National Mission on Enhanced Energy Efficiency.
This is a scheme that contains all the major Energy Intensive sectors across PAN India and REC(Renewable Energy Certificate) that are used to track renewable energy from the point of generation to the purchaser of green power.
This will include encouraging the participants and connecting the markets to a voluntary carbon market.
Second Stage- Strengthening India’s Carbon Trade Market
The second stage will cater to the supply in the market. This stage will include project registrations, their verification, validation, and lastly the issuance of emission reduction units.
The participants will be provided with project-specific reference cases. The performance will be analyzed and evaluated and then the credits will be issued by the regulatory body.
Final Stage- Advanced Mandates for India’s Carbon Trade Market
In this stage, the cap and trade system will come into action allotting the companies’ emissions allowances. Further, this will get aligned with India’s climate commitments and targets.
These will be the three phases of setting up a Carbon Trade Market in India. This method is considered to be the most effective in controlling carbon emissions than the other methods of imposing taxes, penalties, and creating awareness.
In the corporate world today, every other company is aiming for decarbonization and net zero carbon emissions. The government’s step toward setting up a Carbon Trade Market will also help the company to achieve its targets and minimize carbon emission costs.
The company will be encouraged to save the environment and will get benefited by selling its excess carbon credits to other companies. It is high time businesses take ownership of the environmental mishaps that have been generated over the years, which have led to complete environmental devastation at all corners of the globe.
Read also: Business Ecological Model: Reducing Carbon emissions In Business Through Responsible Thinking